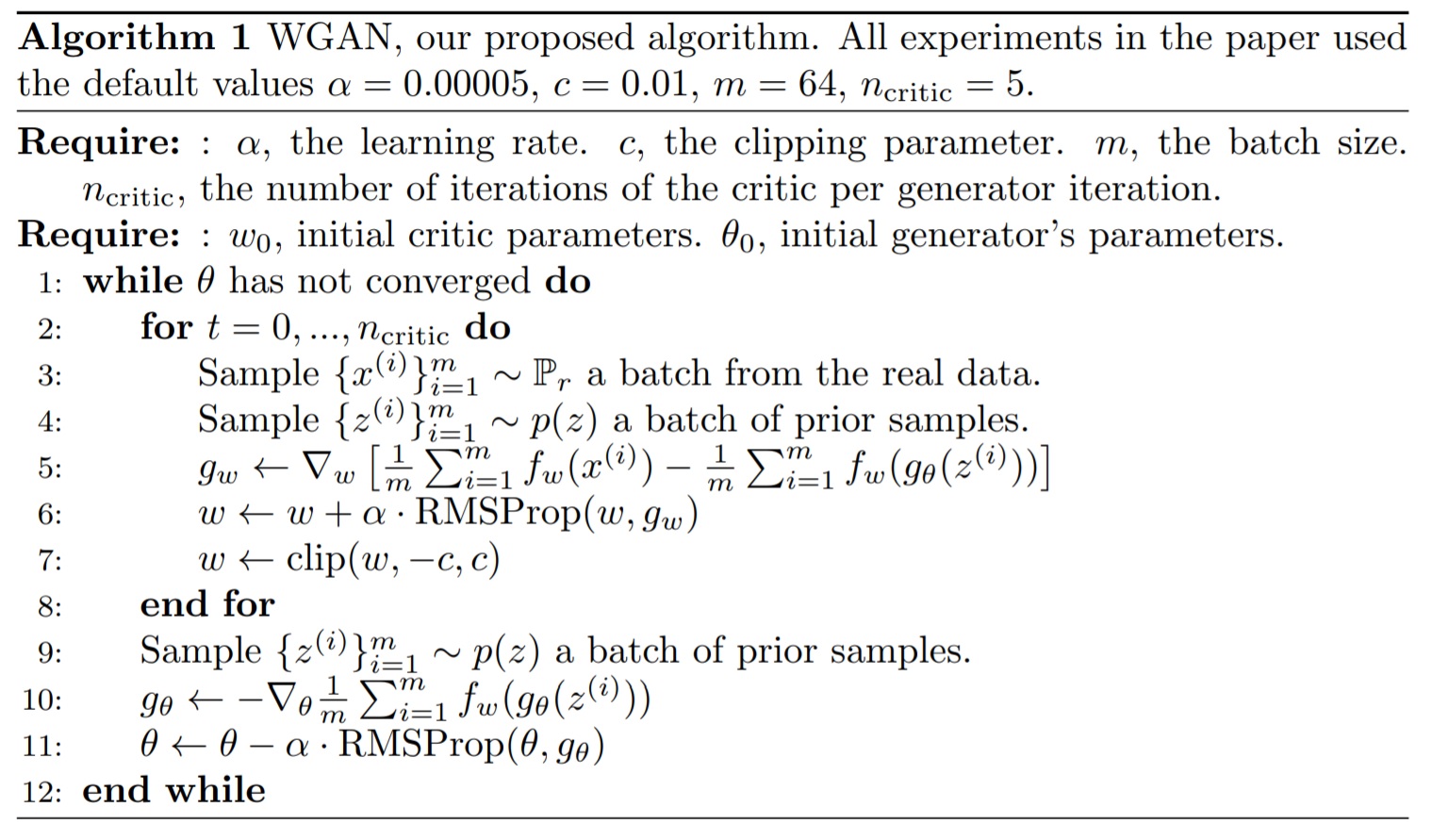
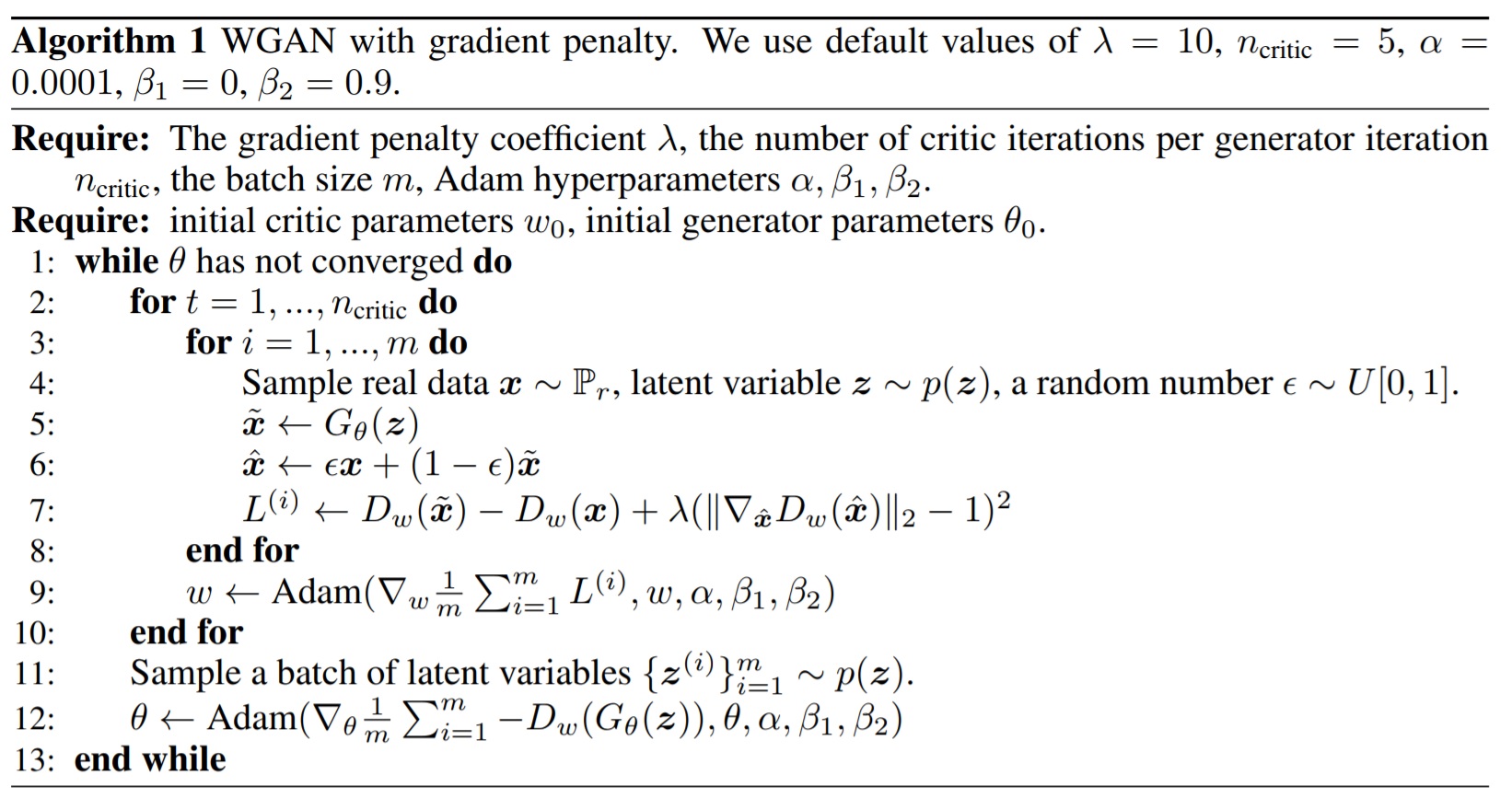
def GAN(img_shape, z_dim):
# x-shape
xh, xw, xc = img_shape
# z-shape
zh = xh // 4
zw = xw // 4
# return Generator and Discriminator
return keras.Sequential([ # Generator
keras.layers.Dense(units = 1024, input_shape = (z_dim,)),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.ReLU(),
keras.layers.Dense(units = zh * zw << 8), # zh * zw * 256
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.ReLU(),
keras.layers.Reshape(target_shape = (zh, zw, 256)),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(
filters = 32,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = 2,
padding = "SAME"
),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.ReLU(),
keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(
filters = xc,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = 2,
padding = "SAME",
activation = keras.activations.sigmoid
),
]), keras.Sequential([ # Discriminator
keras.layers.Conv2D(
filters = 32,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = (2, 2),
padding = "SAME",
input_shape = img_shape,
),
keras.layers.LeakyReLU(),
keras.layers.Conv2D(
filters = 128,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = (2, 2),
padding = "SAME"
),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.LeakyReLU(),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(units = 1024),
keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
keras.layers.LeakyReLU(),
keras.layers.Dense(units = 1),
])
s = tf.random.normal([SAMPLE_NUM, Z_DIM])
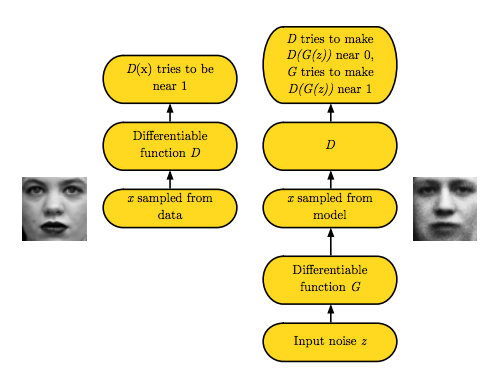
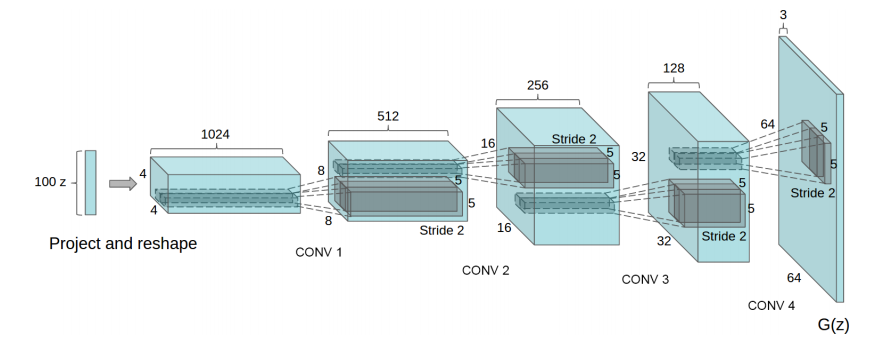 Some suggestions in DCGAN(referenced from paper):
Some suggestions in DCGAN(referenced from paper):